| Home | About | Software | Documentation | Support | Outreach | Ecosystem | Dev | Awards | Team & Sponsors | |
Grid Scheduling Infrastructures Based on GridWay
Most of current meta-schedulers are simple user-level tools that provide basic scheduling, based on match-making, and job management functionality. This means that there is one scheduling instance for each user, and all scheduling instances compete with each other for the available resources. Such user-level meta-scheduling approach exhibits technical and socio-political difficulties within an organization, namely: the end users are responsible for the installation and administration of the meta-scheduler, a Globus client installation is required in each end-user system, firewall configuration must allow traffic between grid resources and end user systems, and the system manager is not able to define job and resource prioritization policies.
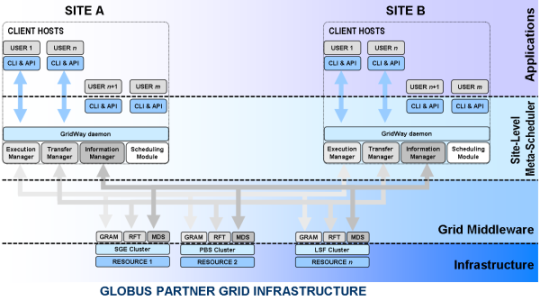
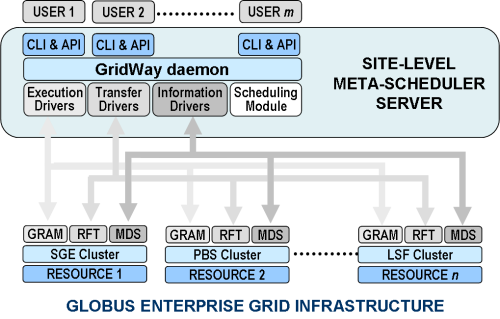
However, a single GridWay scheduling instance, managed by the system administrator, provides support for multiple users to submit, control and monitor their jobs from a front-end or from submission hosts (that do not require either GridWay orGlobus installation), allowing the definition of state-of-the-art scheduling policies.
A. Partner Grid Infrastructures
Partner grid infrastructures of several scales are being deployed within the context of different research projects, whose final goal is to provide large-scale, secure and reliable sharing of resources among partner organizations and supply-chain participants. Such partner grids allow access to a higher computing performance to satisfy peak demands and also provide support to face collaborative projects. The multiple administration domains existing in a partner grid infrastructure prevent the deployment of centralized meta-schedulers, with total control over client requests and resource status. Organization-level meta-schedulers provide support for multiple intra-organization users in each scheduling instance. This means that there is one scheduling instance for each organization, and all scheduling instances compete with each other for the available resources
B. Enterprise Grid Infrastructures
Enterprise grids enable diverse resource sharing to improve internal collaboration and achieve a better return from information technology investment. Available resources within a company are better exploited and the administrative overhead is minimized by using Grid technology. The resources are part of the same administrative domain. Theses infrastructures require a centralized approach for scheduling and accounting. The administrator must be able to apply centralized usage policies and access to global reporting and accounting. Enterprise grid infrastructures require meta-schedulers to provide support for multiple users in a single scheduling instance.
C. Federation of Grid Infrastructures
Please visit the web page about Federation of Grid Infrastructures and Utility Computing to find out how to deploy federated grid infrastructures using Globus and GridWay. A WS-GRAM service hosting a GridWay meta-scheduler provides the standard functionality required to implement a gateway to a federated grid. That is to virtualize a whole grid, providing a powerful abstraction of the underlying grid resource management services.